Sharding
A simplified reference
Sharding. Sounds similar to another word…
Sharding is a word that has been bouncing around in the crypto space, especially in reference to Ethereum 2.0.
Let’s grab a high-level definition:
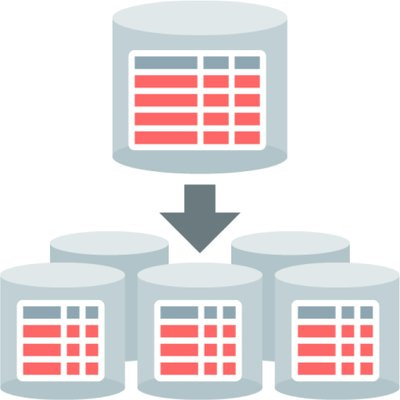
Sharding is a database partitioning technique used by blockchains with the purpose of scalability, enabling them to process more transactions per second.
Background
Sharding was a technique originally derived by database engineers.
Databases hold a ton of info, and there are risks and limitations to this. So database engineers realized they needed to split up the data so they could store it safely, securely, and make sure the equipment they had could store it. They split the data up and stored it on multiple pieces of hardware.
Crypto application
In terms of crypto, sharding splits a blockchain’s entire network into smaller partitions, known as “shards.”
Each shard is comprised of its own data. It is independent and distinct from other shards.
Sharding helps reduce the latency (slowness) of a network since it splits a network into separate shards.
This considerably increases the blockchain’s scalability (Txns/per sec).
Use case
Let’s go through a real-world example with Ethereum as our use case:
Right now, the Ethereum network is very congested, meaning a bunch of people want to transact on it. The ETH blockchain handles 15 transactions per second. ETH uses a bidding system to place your transaction on a block, and competition drives the price up, making it expensive to transact on ETH.
To fix this, Ethereum plans to implement sharding. There will be 64 shards (blockchains) that can accommodate a much higher transaction throughput. This is a big deal, because most blockchains that handle a high transaction throughput are very centralized. Read more about this by searching “blockchain trilemma.”
Next, sharding improves the physical storage of the blockchain. Currently, there are ETH nodes. These nodes are actual computers that keep a record of the Ethereum blockchain. This record grows significantly as time moves and popularity skyrockets. Sharding allows computers to keep smaller records, because these computers are selected to verify specific shards rather than the ETH blockchain in its entirety. This has the added bonus of reducing the physical hardware requirements to participate in securing the network, a democratic and accessible effect.
Finally, these computers or nodes are selected randomly. This randomization prevents bad actors from manipulating transactions, so sharding improves the security of the network.
Summary
All in all, sharding improves blockchains in the following ways:
• more transactions per second
• scalability without centralization
• network is harder to attack
• physical requirements to participate in securing the network are more affordable
I hope this is helpful.

Fantastic overview! 🤝